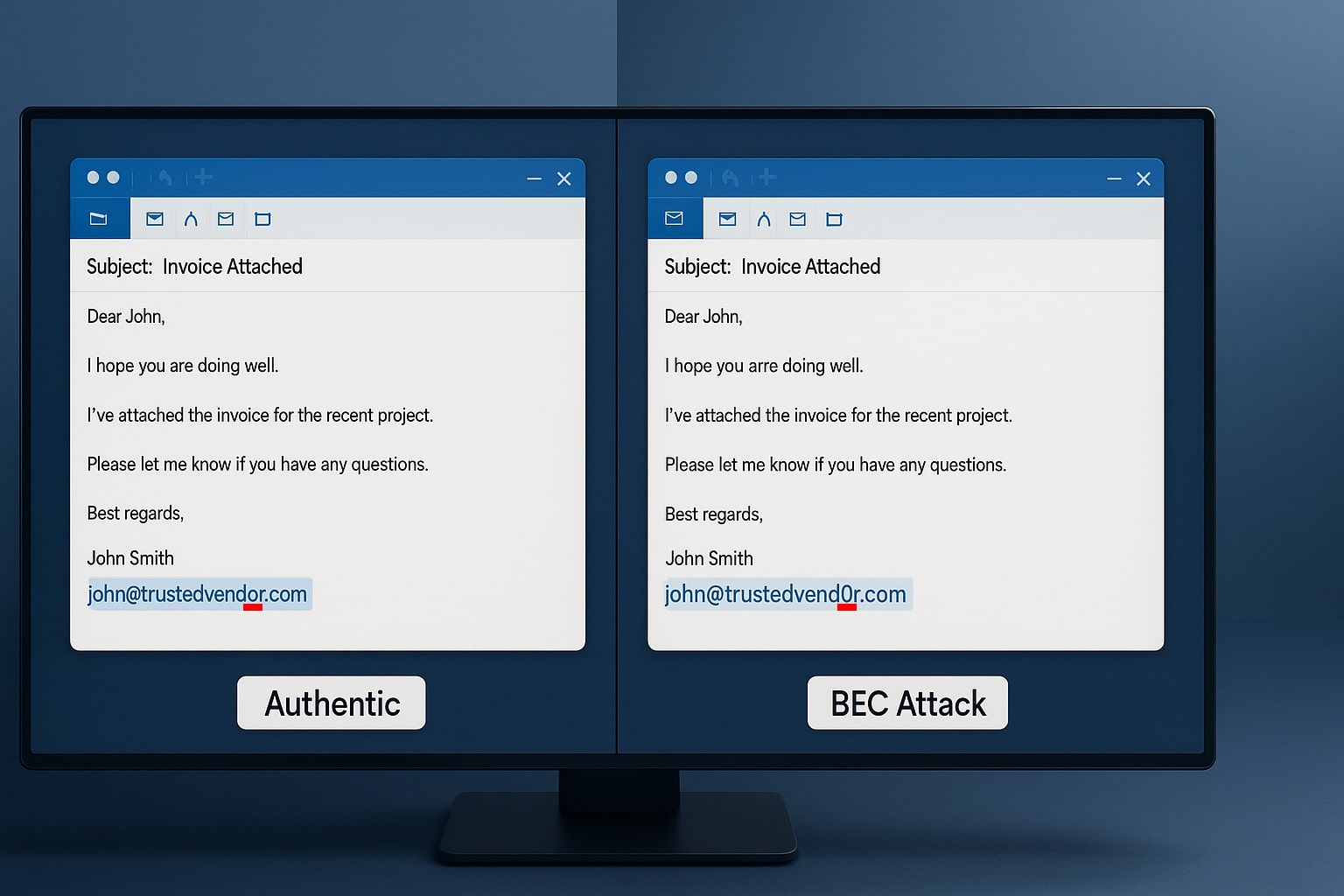
Network security is a pressing issue for organizations today. With increasing cyber threats and attacks, it’s important for businesses to implement the best practices in network security to prevent data breaches. In this article, we will discuss the top network security best practices that every organization should follow.
From securing passwords to implementing firewalls, we will provide insights on how to keep your networks secure and protect sensitive information from potential hackers. So, if you’re interested in making sure your company’s network is safe from cyber threats, read on as we dive into everything you need to know about network security best practices.
Need to Keep Your Network Protected?
Secure Password Policies: Creating Strong and Unique Passwords
Creating strong and unique passwords is one of the most fundamental ways to prevent cyber attacks in any organization. Using passwords that are easy to guess or reuse across multiple accounts makes it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access to networks and systems. Therefore, implementing a secure password policy is crucial for network security. Organizations should encourage their employees to create complex passwords with at least 12 characters, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols.
In addition to creating strong passwords, organizations should also implement measures that promote good password hygiene such as changing passwords frequently and prohibiting the use of personal information like names or birthdates in the password creation process. The use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) can also enhance security by requiring an additional verification step beyond just a password when logging into company accounts. Following secure password policies will greatly contribute towards creating a safer network environment for organizations against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Protecting Against External Threats: Firewalls and Anti-Malware
When it comes to protecting against external threats, firewalls and antivirus software are two essential tools in any organization’s arsenal. A firewall acts as a barrier between an internal network and the internet, monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic for signs of suspicious activity. Meanwhile, antivirus software scans for malware, viruses, and other malicious code that could potentially compromise sensitive data.
However, it’s not enough to rely on just one type of security solution – combining multiple layers of protection is key to ensuring the highest level of network security. Anti-malware solutions can provide additional protection against various types of cyber threats such as phishing attacks or spyware. By implementing these different security measures effectively, organizations can improve their chances in thwarting potential attacks and safeguarding critical information from external adversaries.
Network security practices require a multi-layered approach that involves utilizing powerful firewalls alongside advanced antivirus and anti-malware solutions. With comprehensive protection like this in place businesses can rest easy knowing they’ve done everything possible to protect their networks from external threats that may compromise valuable assets or confidential data about clients or employees alike.
Need to Keep Your Network Protected?
Managing User Access: Role-Based Authentication
Managing user access is a critical component of network security. Role-based authentication and least privilege principles are two best practices that can help organizations mitigate risk and protect against data breaches.
Role-based authentication allows businesses to assign specific roles to individual users, which determine their level of access to sensitive information within the network. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access by restricting users’ permissions based on their role in the organization. Additionally, regular updates should be made to ensure that roles remain current and relevant.
The principle of least privilege requires limiting user privileges only to what they need for their job function, reducing potential exposure points for cyberattacks. By following this principle, companies can minimize damage caused by insider attacks or mistakes made by high-privilege users. Together, these two strategies form a comprehensive approach towards effective user management that helps safeguard an organization’s IT infrastructure from cyber threats while also ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Staying Up-to-Date: Regular Software Updates and Security Patches
One of the key best practices in network security is staying up-to-date with regular software updates and security patches. It’s not uncommon for vulnerabilities to be discovered in software applications, and these weaknesses can leave your organization exposed to cyber attacks. By regularly updating your software and implementing security patches, you can reduce the likelihood of a breach occurring.
In addition to reducing vulnerability, updating software also provides new features that may improve the functionality of your systems or address bugs that were previously problematic. Many operating systems have automatic update settings which organizations should enable to ensure their devices are always up-to-date with the latest security protocols.
Committing to regular updates requires discipline from everyone within an organization – including management who must allocate resources for IT staff members responsible for monitoring and maintaining patch schedules. However, this investment will pay dividends by helping businesses prevent data breaches and stay competitive against evolving online threats.
Employee Awareness: Educating on Cybersecurity and Best Practices
One key factor in implementing effective network security practices is employee awareness. Educating staff on the various risks associated with network security and training them on best practices can go a long way in preventing data breaches. It’s important for employees to understand the potential consequences of not taking proper precautions when accessing company networks or using personal devices for work purposes.
There are several ways to educate employees on network security. Regular training sessions, informational emails, posters around the office, and providing access to resources such as guidelines and policies can all help raise awareness. However, it’s essential that these efforts are ongoing rather than isolated events so that employees remain informed about current threats and understand why certain procedures are necessary.
By prioritizing employee education and promoting a culture of vigilance around network security risks, companies can reduce their risk of being targeted by cybercriminals who often exploit human error as an entry point into sensitive systems. This helps preserve customer trust and protects against reputational damage resulting from a breach in data confidentiality or integrity.
Need to Keep Your Network Protected?
Implement Best Practices Today
As we have discussed, network security is a crucial aspect that every organization must prioritize. It’s important toe implement best practices when it comes to securing your company’s networks and protecting confidential information from cyber threats. Be sure to focus on creating robust password policies, regularly updating software and operating systems, utilizing firewalls, implementing access controls, and conducting regular vulnerability assessments.
By following these best practices for network security, your organization can reduce the risk of data breaches and prevent sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. However, it’s important to note that cybersecurity threats are always evolving. Your company should continuously review your security protocols to act quickly against any potential threats or attacks. In doing so you’ll be able to protect your business reputation as well as safeguard your customers’ personal data in today’s technology-driven business environment.
Related Posts

Law Firms Beware: The Silent Ransom Group is Calling
read more
Slopsquatting: The AI Security Threat Every Development Team Must Address
read more