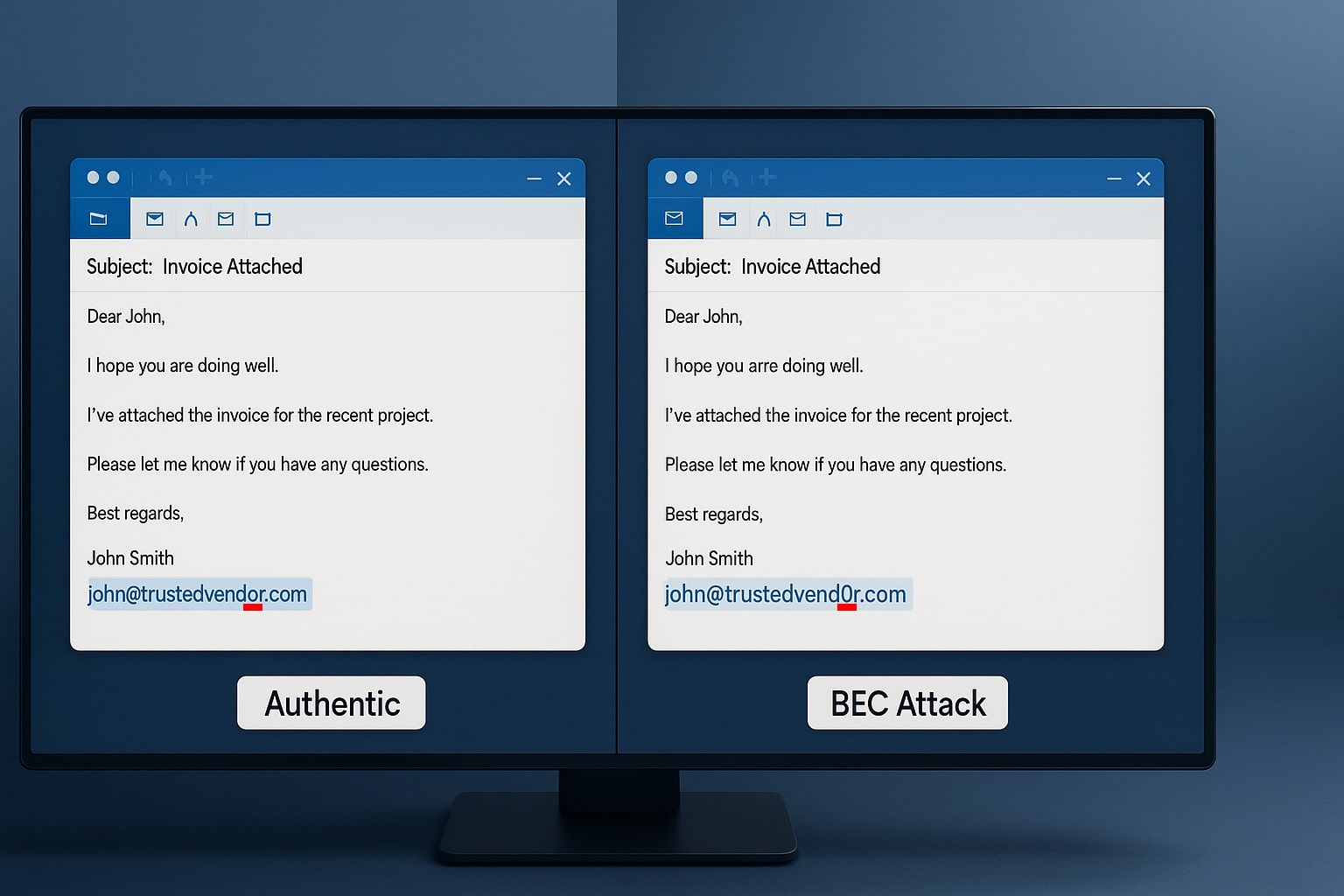
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) fatigue is a growing cybersecurity threat where attackers repeatedly send second-factor authentication requests to victims’ email, phone, or registered devices. This is known as MFA Bombing or MFA Spamming. The attackers’ goal is to coerce the victim into confirming their identity via notification, thereby authenticating the attacker’s attempt to enter the victim’s account or device.
MFA fatigue attacks are often preceded by other social engineering attack vectors, such as phishing, to gain credentials. Stolen credentials may also be acquired from the dark web and via other attack vectors.
Need to Keep Your Business Protected?
Most modern MFA platforms support push-notification style authentication, where users receive a push notification asking them to confirm their second factor authentication after submitting their initial set of credentials. In theory, this allows users to authenticate their identity through a single phone notification and often a single tap on the screen.
The prevalence of this simplified authentication architecture is what’s causing MFA fatigue attacks to grow in popularity among hacking groups. MFA fatigue attacks often result in depositing ransomware software, taking corporate resources or sensitive data hostage in exchange for a monetary ransom.
An MFA fatigue attack begins with user information already available, including the victim’s username, password, or recovery credentials. This information is usually sourced from preliminary attacks such as phishing or social engineering or may have been exposed credentials from a larger breach. Stolen information can also be purchased on the dark web.
The attackers use the illicitly gained credentials to sign in to the victim’s account or device secured by push multi-factor authentication. They then attempt to activate the authenticating application’s push notifications in quick succession, which can occur over email, text message, or desktop notification, but are generally pushed to the user’s authenticated mobile device.
The victim will rapidly receive push notifications, as the attacker attempts to overwhelm them. The goal is for the victim to push “Yes” and confirm their identity, permitting the attacker to venture further into their account or device. The attacker may pose as a tech support employee, contact the victim and attempt to explain that the push notifications are part of a normal maintenance procedure, as reportedly happened in the Uber breach by Lapsus$.
Need to Keep Your Business Protected?
To protect against MFA fatigue attacks, organizations should educate their employees on the risks of social engineering attacks and the importance of maintaining good cybersecurity practices. They should also implement secure and consistent multi-factor authentication policies across all systems and applications. By doing so, organizations can prevent MFA fatigue attacks and reduce the risk of cyber threats.
Stay Alert & Think Twice
Before you give up on the beeping noises from your phone and click, “APPROVE” – STOP AND THINK TWICE!
If you need help with Cyber Security training or want to outsource your Cyber Security experts, don’t hesitate to contact us today. We’re only a phone call away – 561-282-2225
Related Posts

Law Firms Beware: The Silent Ransom Group is Calling
read more
Slopsquatting: The AI Security Threat Every Development Team Must Address
read more